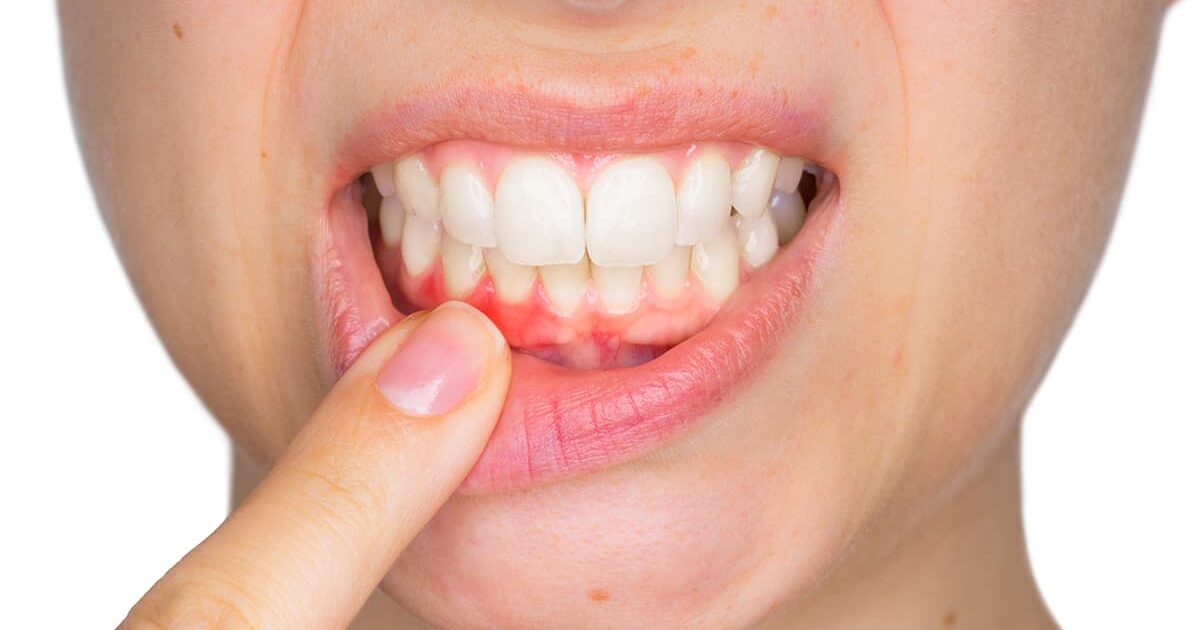
Periodontal disease is the most common chronic inflammatory disorder of the oral cavity. This is considered the leading cause of tooth loss if not treated promptly. It may begin as a mild infection but may progress to destroy the underlying jawbone, deteriorating your oral health further.
You can consult the dental specialists at Manassas, VA dental practice if you notice any signs and symptoms of periodontal disease like swollen, bleeding gums or tooth mobility.
An insight into periodontal disease
Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease, is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth that support and anchor them. It typically develops due to the accumulation of dental plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on teeth.
| Stages:
Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease and is characterized by inflammation of the gums. Gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene practices and professional dental cleanings. Periodontitis: If gingivitis is left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis. In this stage, the inflammation extends deeper into the supporting structures of the teeth, including the bone. This stage can result in tooth mobility, bone loss, and, if severe, tooth loss. |
Potential causes of periodontal disease
Bacteria is the most common etiological factor that, when left untreated, can lead to the formation of plaque that adheres to the tooth surfaces. This paves the way for increased bacterial infiltration that eventually hardens to form calculus. As the infection spreads, it can erode the gums and destroy the underlying jawbone.
Risk Factors:
|
Symptoms of periodontal disease
- Red, swollen gums
- Tender, painful gums
- Persistent bad breath (halitosis)
- Pain when chewing
- Poor bite due to malocclusion
- Receding gums
- Increased tooth sensitivity
- Loose teeth
Periodontal disease treatment
Treatment options include:
Non-surgical options:
- Professional dental cleaning
- Antibiotic gels
- Antimicrobial mouth rinse
- Enzyme suppressants
- Gingival pocket irrigation
Surgical options:
- Pocket elimination surgery
- Tissue regeneration
- Gum grafting
- Bone grafting
- Dental implants
Preventing periodontal disease
Here are some key strategies to prevent periodontal disease:
- Regular oral hygiene through brushing and flossing
- Regular dental checkups
- Eating a healthy diet
- Avoiding tobacco use
- Limiting alcohol consumption
- Managing stress
- Staying hydrated
- Maintaining systemic health like diabetes and hypertension
Conclusion
Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing periodontal disease and preventing its progression to more severe stages. Regular dental check-ups and communication with a dentist can help address any concerns and ensure optimal oral health.