Tick-borne illnesses, including Lyme disease, can have significant impacts on health if left untreated. For professionals balancing demanding schedules, recognizing early symptoms is crucial to preventing long-term complications. Being aware of potential warning signs and understanding when to seek medical evaluation ensures timely and effective treatment.
The Basics of Tick-Borne Illnesses
Ticks are tiny arachnids that can carry bacteria, viruses, and parasites capable of causing disease in humans. Lyme disease is the most well-known tick-borne illness, but other conditions, such as anaplasmosis, babesiosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis, also pose health risks.
Each of these illnesses presents with a range of symptoms, many of which overlap, making diagnosis challenging without proper medical evaluation.
Early Warning Signs of Tick-Borne Illnesses
1. Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted through the bite of infected black-legged ticks. Key early symptoms include:
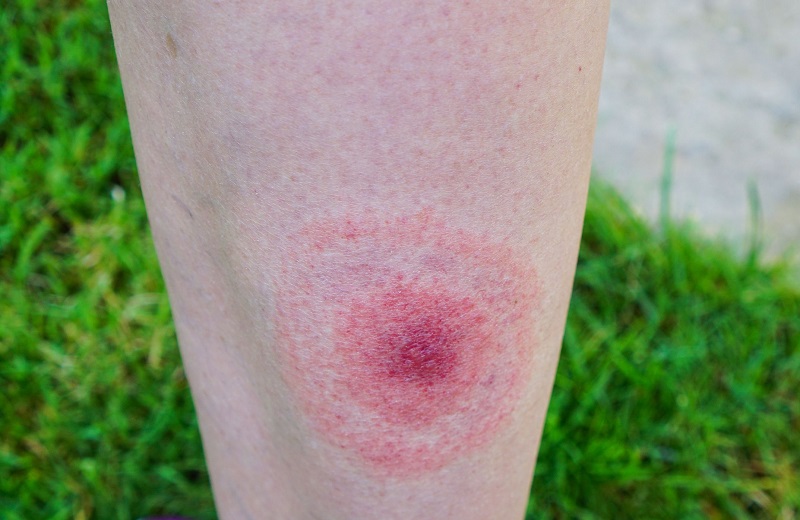
- Erythema Migrans (EM) Rash: Often referred to as a “bullseye” rash, this expanding red area may appear at the site of the tick bite. However, not everyone with Lyme disease develops this rash.
- Flu-Like Symptoms: Fatigue, fever, chills, muscle aches, and headache can mimic a typical viral illness, making early detection tricky.
- Joint Pain: Early joint discomfort, particularly in large joints like the knees, may occur as the bacteria spreads.
2. Anaplasmosis and Ehrlichiosis
Both diseases are bacterial infections transmitted by ticks and present with similar symptoms:
- Fever and Chills
- Severe Headache
- Muscle Aches
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms: Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea may occur.
Without treatment, these illnesses can progress to more severe complications, including respiratory distress and organ damage.
3. Babesiosis
Babesiosis is caused by parasites that infect red blood cells, leading to:
- Fatigue and Weakness: Due to the destruction of red blood cells.
- Fever, Chills, and Sweats
- Anemia and Jaundice: Paleness or yellowing of the skin may indicate a more severe infection.
4. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
RMSF is a bacterial illness that can cause life-threatening complications if untreated. Symptoms include:
- High Fever and Severe Headache
- Rash: Red, spotted rashes often appear on the wrists, ankles, or palms and spread over time.
- Abdominal Pain or Confusion: These symptoms suggest severe progression and warrant immediate medical attention.
When to Seek Help
Because symptoms of tick-borne illnesses overlap with other conditions, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation if you’ve had potential exposure to ticks—particularly during outdoor activities in wooded or grassy areas—and experience symptoms like those listed above.
Timing is Critical
Prompt diagnosis and treatment are key to avoiding long-term complications, such as chronic fatigue, neurological issues, or persistent joint pain associated with untreated Lyme disease or other tick-borne conditions.
If you suspect Lyme disease or another tick-borne illness, your healthcare provider may recommend a Lyme disease test or other diagnostic evaluations to confirm the infection. Tests typically involve blood work to detect specific antibodies or markers of the disease. While no single test is foolproof, these tools are invaluable in guiding effective treatment plans.
Steps for Reducing Risk
Understanding how to prevent tick-borne illnesses is as important as recognizing their symptoms. Here are practical steps to reduce your risk:
- Dress for Protection: Wear long sleeves, long pants, and closed-toe shoes when spending time in tick-prone areas. Light-colored clothing makes it easier to spot ticks.
- Use Tick Repellents: Products containing DEET, permethrin, or other EPA-approved repellents can reduce the likelihood of tick bites.
- Conduct Tick Checks: After outdoor activities, thoroughly check your body and clothing for ticks. Pay close attention to hidden areas like the scalp, underarms, behind the knees, and the waistband.
- Remove Ticks Properly: Use fine-tipped tweezers to gently remove ticks as close to the skin as possible. Clean the bite area with antiseptic after removal.
Holistic Care for Tick-Borne Illnesses
If diagnosed with a tick-borne illness, a comprehensive care approach can help manage symptoms and speed recovery:
1. Antibiotic Therapy
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial tick-borne illnesses like Lyme disease, anaplasmosis, and ehrlichiosis. Early intervention typically results in a full recovery.
2. Supportive Therapies
For illnesses like babesiosis, treatment may also include antimalarial medications to address parasitic infections. Supportive care, such as rest and hydration, is critical for recovery.
3. Long-Term Monitoring
While most cases resolve with treatment, some individuals experience lingering symptoms, sometimes referred to as Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome (PTLDS). Working closely with a healthcare provider ensures proper management of long-term effects.
Advocating for Your Health
For busy professionals, it’s easy to overlook early symptoms of tick-borne illnesses or delay seeking care. However, prioritizing your health is essential for sustained productivity and overall well-being. Being proactive in recognizing potential warning signs and seeking timely medical evaluation can prevent more serious complications.
Tick-borne illnesses are manageable when caught early, but they require vigilance and awareness. By educating yourself on the symptoms and risk factors, you can take control of your health and protect yourself against the long-term impacts of these conditions.