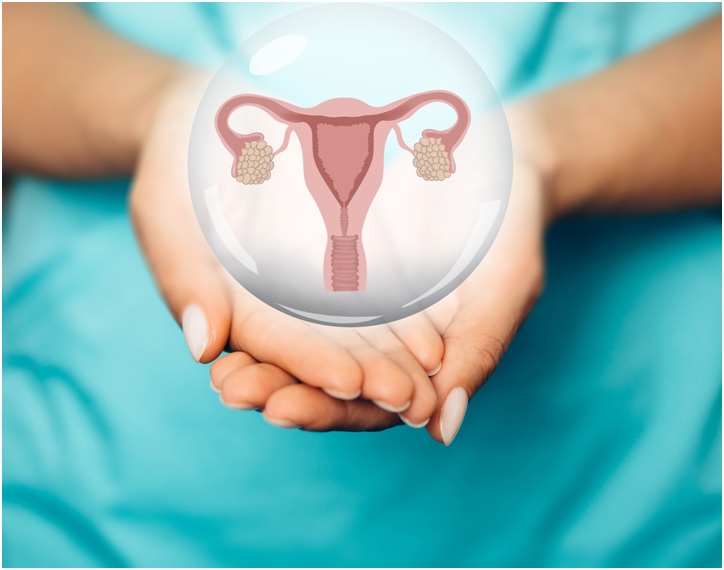
Postinor 2 will not destroy the womb or any other reproductive organs. The contents of postinor 2 are levonorgestrel as the active and main ingredient, potato starch, talc, maize starch, lactose monohydrate, silica colloidal anhydrous, magnesium stearate.
Levonorgestrel is a synthetic form of sex hormone which is dominant in females. The consumption of postinor 2 will prevent and stop the fertilization and ovulation. Fertilization and ovulation are part of the reproductive cycle and essential for a female to get pregnant. Postinor 2 is effective in preventing up to 85% of expected pregnancy.
Overdosage of this medication may cause withdrawal bleeding and nausea. Those who are allergic to levonorgestrel or the excipients should not take this medication as a form of emergency contraception. Excipients are the inactive ingredients within a medication which help to stabilize the active ingredient. The excipients as mentioned above are all the contents of postinor 2 except levonorgestrel.
Postinor 2 is also not suitable for lactose intolerance individuals and pregnant ladies. It is not a method of abortion! Postinor 2 also should not be taken by lactating mothers. This medication may alter the regularity of your menses and interfere with your date of ovulation.
Postinor 2 is a type of contraception. It is an oral medication use as an emergency contraception following:
- Unprotected sexual intercourse
- Failure of other forms of the contraceptive method such as condom breakage
The disadvantages of levonorgestrel are:
- Only effective if taken within 72 hours
- Not suitable for lactose intolerance individuals
- Not a form of abortion
- 15% of failure rate
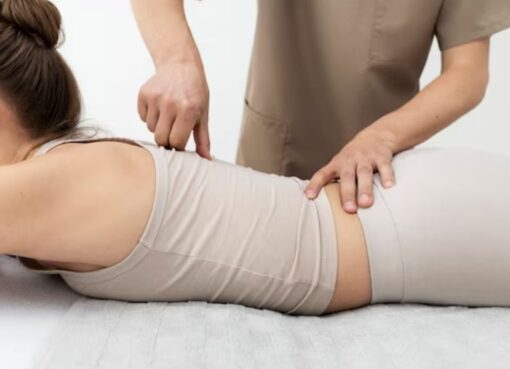
Postinor 2 will only be effective if consumed within 72 hours following unprotected sexual intercourse or failure of contraceptive method. During pregnancy, many changes will take place. There will be physical, emotional, and hormonal changes. Normal changes are expected throughout pregnancy. On the other hand, abnormal changes will require medical intervention. Due to many changes, the musculoskeletal system is one of the body systems which will be affected. Pregnant ladies may develop back pain, generalized joint pain, and tendonitis (inflammation of the tendons). Pregnancy will cause a woman to gain around 11 to 15 kg. Weight gain, shifting of the center of the gravity, and hormonal changes will cause alteration and straining to muscles and joints.
The musculoskeletal changes that happened to a pregnant lady are:
- Fluid retention that may compress vital structures like the nerves
- The curvature of the lower back increases
- Forward bending of the neck
- Instability of the spine due to increase joint laxity results in straining of the back muscles
- Vaginal lengthening and genital widening
- Stability of the joints from the pelvis to the feet will be affected due to increased laxity of the ligaments
- The shoulders shifted downwards
- Stretching of the abdominal muscles strain the muscle of the back even more
- The force and pressure to some joint might increase up to two folds
Other alternatives to levonorgestrel as emergency contraception are:
- Ulipristal acetate
- Copper intrauterine device (IUD)
Both ulipristal acetate and copper intrauterine device are effective if taken up to 5 days after unprotected sex or fail of barrier contraception.
This medication should be stored below 30 degrees celsius and away from sunlight. Pregnancy is a state where the implanted product of conception develops into a fetus usually inside the uterus of the mother. Pregnancy is usually suspected when there’s a delay in period or menses in women of reproductive age. The symptoms of early pregnancy are:
- Constipation
- Nasal congestion
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea and vomiting
- Breast enlargement
- Breast tenderness
- Frequent urination
- Tiredness or fatigue
- Uterine discomfort or cramps
- Bloated abdomen
- Heartburn
- Cravings for food or drinks
- Mood swings
- Lightheadedness
- Low back pain
- Difficulty in sleeping
- No menses or amenorrhoea