Anxiety therapy is a form of psychotherapy that aims to help individuals reduce anxiety symptoms and improve their overall well-being. There are various types of anxiety therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and mindfulness-based therapies.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a form of therapy that focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors that contribute to anxiety symptoms.
- Exposure therapy involves gradually exposing the individual to the things they fear and avoid, in a controlled and safe environment, to help them learn to manage their anxiety.
- Mindfulness-based therapies such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) and Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) teach individuals to focus on the present moment rather than dwelling on past experiences or worrying about the future.
It’s important to note that anxiety therapy in London may not be suitable for everyone, and different people may respond better to different types of treatment. It’s best to consult with a mental health professional to help determine the best course of treatment for your specific needs.
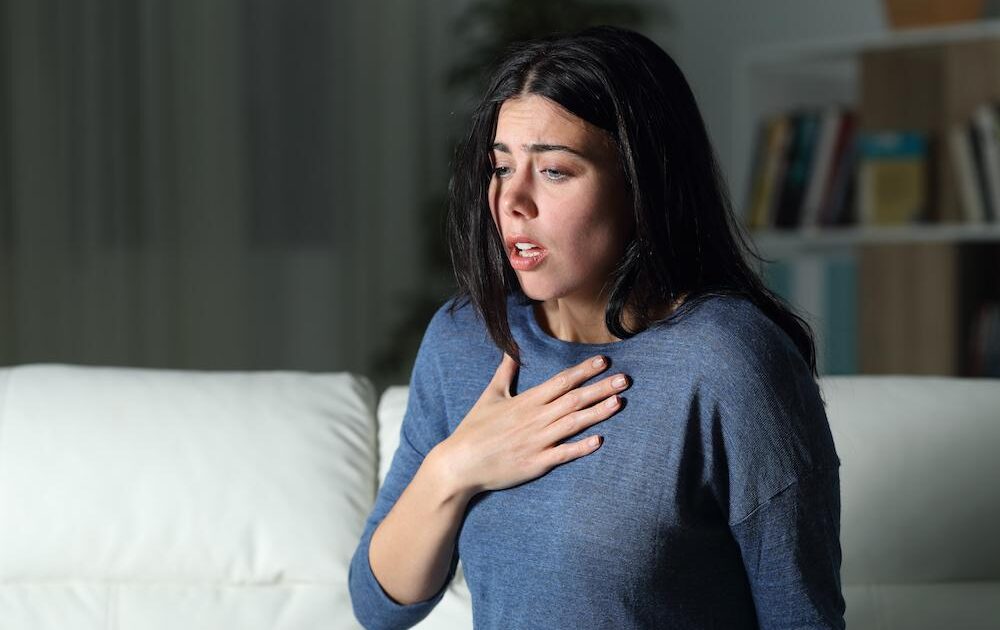
Anxiety can manifest in various physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. Some common signs of anxiety include:
- Physical symptoms: Rapid heartbeat, sweating, trembling, muscle tension, fatigue, headaches, and stomach upset
- Emotional symptoms: Fear, worry, restlessness, irritability, and feelings of panic or dread
- Behavioral symptoms: Avoiding certain situations or activities, difficulty concentrating, difficulty sleeping, and changes in appetite or weight.
Some other signs of anxiety can include constant anticipation of disaster, being easily fatigued, difficulty controlling worry, difficulty concentrating, muscle tension, sleep disturbance, and difficulty falling or staying asleep.
Anxiety is a normal emotional response to stress, but it can become excessive and disruptive to daily life. There are several potential causes of anxiety, including:
- Genetics: Anxiety disorders can run in families, suggesting a genetic component.
- Trauma: Traumatic events, such as abuse, neglect, or major life changes, can lead to the development of anxiety disorders.
- Brain chemistry: Anxiety can be caused by imbalances in the chemicals in the brain that regulate mood.
- Medical conditions: Some conditions, such as thyroid problems, can lead to anxiety symptoms.
- Substance abuse: Certain substances, including alcohol and drugs, can lead to anxiety.
It’s important to note that anxiety can be caused by a combination of factors, not just one. It’s best to consult a mental health professional to get a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Anxiety treatment options
These are some of the treatment options:
- Medications: Antidepressant medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and anti-anxiety medications, such as benzodiazepines, can help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Therapy: Various forms of treatment, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and mindfulness-based therapies, can help individuals learn to manage their anxiety and change negative thought patterns.
- Lifestyle changes: Changing diet, exercise, and sleep patterns can help reduce anxiety symptoms.
- Relaxation techniques: Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can help to reduce stress and anxiety.
- Support groups: Talking to others with similar experiences can be a helpful form of support and provide a sense of community.
- Complementary therapies: Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and herbal supplements may be used in conjunction with other forms of treatment.
It’s important to note that different people may respond better to different types of treatment, and it may take some trial and error to find the most effective treatment plan.