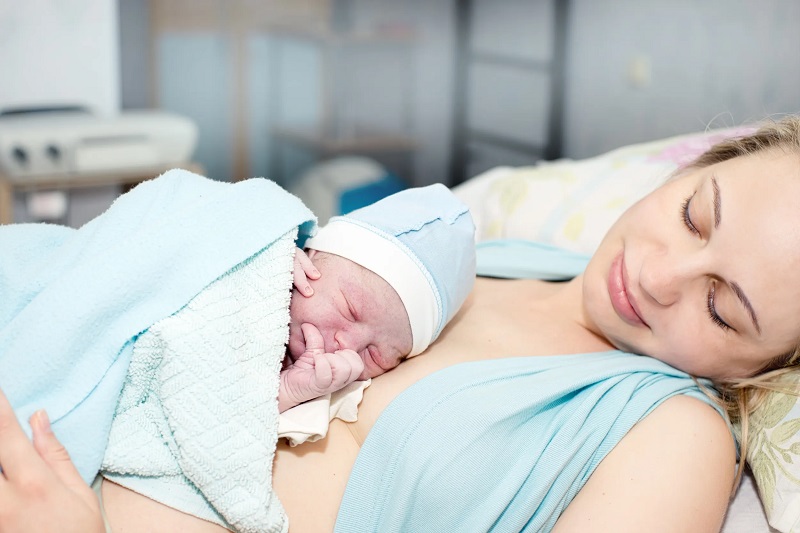
When anything bad happens during labour and delivery, whether it’s physical or not, we call it “birth trauma,” and it may affect both the mother and the newborn. Trauma at birth is a common cause of permanent health problems, disabilities, and neurological disorders.
We believe that the huge rise in the incidence of chronic illnesses in children in the modern era may be traced back to one factor: birth trauma. The effects on children are both “short term” and “long term.” We often find the following to be linked to traumatic birth experiences:
Breastfeeding difficulties, include difficulty latching and maintaining a good latch
The Problems and Disorders of Sleep
- Constipation, Colic, and Reflux
- Such disorders include torticollis, plagiocephaly, shoulder dystocia, and others.
- Spastic Diplegia of the Brain
- Seizures (from epilepsy) (seizures)
- Autism spectrum disease (ASD), attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and other neurodevelopmental disorders
- Disorders of social and emotional development, as well as delays in language and physical development
- Immune system problems, respiratory illness, and recurrent ear infections
What Leads To Abuse During The Presentation Of The Child?
Trauma during childbirth almost invariably manifests as physical problems. Epidurals, inductions, forceps or vacuum extractions, monitoring of the umbilical chord, and caesarean sections are only some of the various delivery techniques that may lead to this, as they did with Landon. It’s also important to remember that different cases may include different levels of birth trauma. The majority of cases are not recognised nor reported to the standard medical community.
What Does It Mean To Have A Hard Birth?
The aforementioned list demonstrates the breadth and potential connection between birth trauma and every health issue affecting children.
That’s because the central or autonomic nervous system is the primary target of damage from physical (and chemical) birth trauma. The reasoning for this is simple to understand.
When this system’s normal function is interrupted or deviates from its intended path in infancy or early childhood, a disease known as dysautonomia may occur.
To get into the nitty-gritty, the vagus nerve is the key to solving all of these health issues in childhood and old age. The abdominal region is home to this nerve. The vagus nerve coordinates a wide variety of bodily processes, including heart rate, breathing, digestion, immune system function, social and emotional regulation, and much more.
The vagus nerve is the most vulnerable to injury during labour and delivery due to its location. Beginning in the brainstem’s dorsal region, this vital nerve descends via the cervical spine (neck) and chest (thorax) to reach the abdominal cavity. This is why the “wandering” nerve has been a common name for it for centuries.